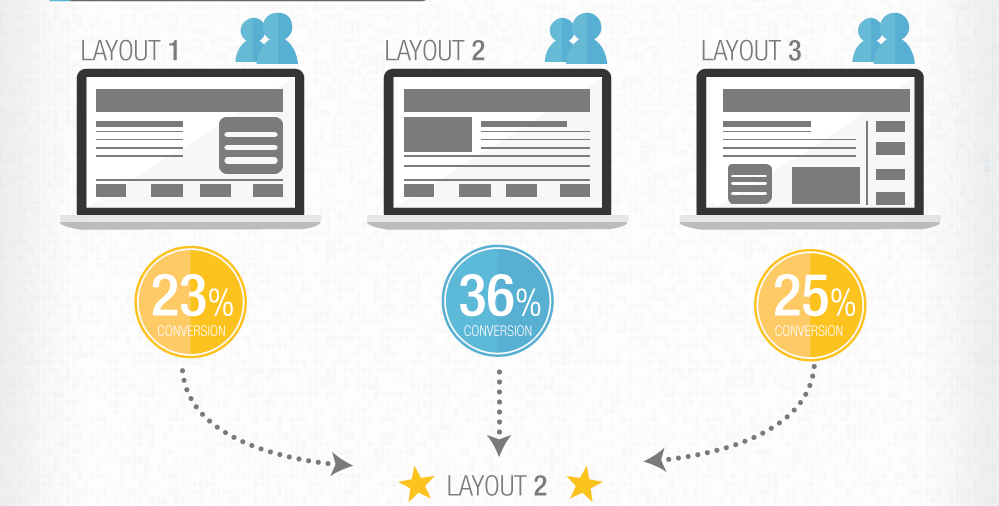
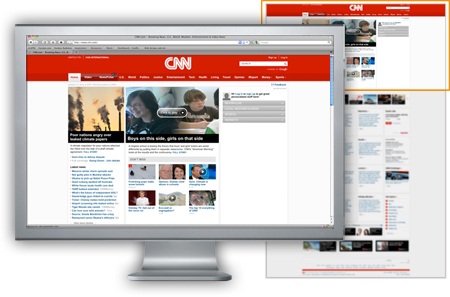
Comparing complex multi-variable systems, especially for understanding market perceptions A process for comparing the effects of multiple components of a website in a live environment. This is essentially many comparison tests performed on one page at the same time. A dynamic website can be used to serve up different versions of a page in equal proportions to visitors. The key …
Lean UX
A design practice which focuses on the end goal and the elimination of unnecessary tasks Lean UX is inspired by lean and agile development theories. It places greater focus on the actual experience being designed, and less on the deliverables. With this approach, traditional documents are stripped down to their bare components to provide the minimum amount of information necessary …
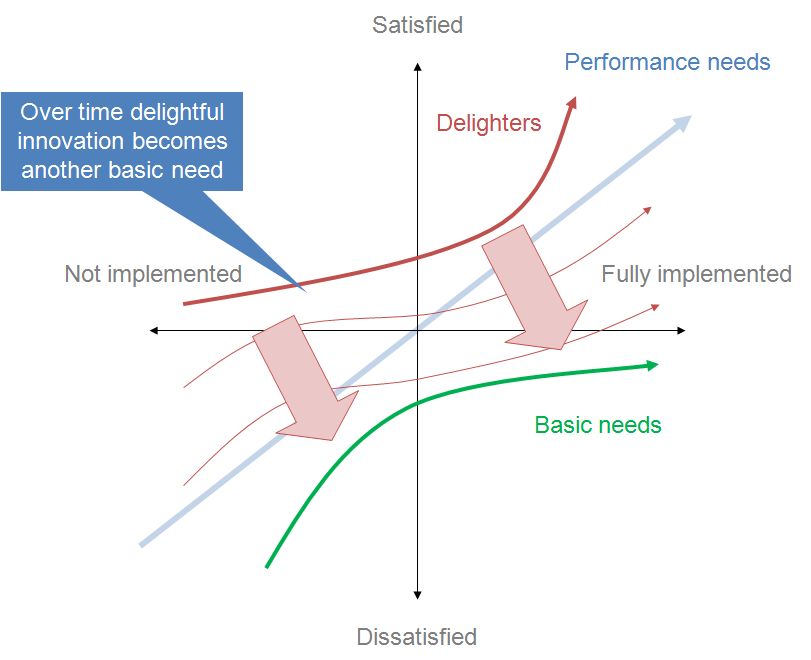
Kano Model
A product development theory that classifies features into five areas to aid prioritization Must-have features are the minimum expected functionality; they are taken for granted. Users will not be excited if they are present, but disappointed if they are absent. One-dimensional features are received differently depending on how fully (or well) they are implemented. Users will be excited if they …
Information Architecture
The organization of a set of information to maximize the ease of locating each piece of information Information architecture (IA) refers to the process of structuring and organizing information to make it easily navigable by users. A well-considered structure is an important part of any system which allows users to browse and add to a large database of information. A …
Hicks Law
The time taken to make a decision increases as the number of options increase Hick’s Law is also known as the ‘Hick-Hyman Law’. In situations where a decision is made between multiple equal options, the time taken is related to the number of options available. A decision between few options will take less time than a decision between many options. …
Heuristic Evaluation
A Method used to identify usability problems, by judging adherence to established usability principles This technique assesses the usability of an interface by examining its compliance with established heuristics, or ‘rules of thumb’ – principles which are widely recognized to improve the usability of a system. For example, a common heuristic states that the user must be able to determine …
Graceful Degradation
Building an application for modern browsers while ensuring it remains functional in older browsers
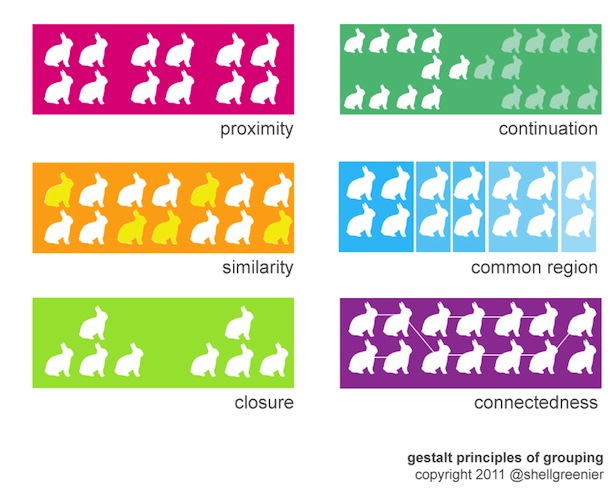
Gestalt Laws of Grouping
A set of principles which describe how humans perceive patterns in objects Proximity: when elements are placed near to each other, they are perceived to be grouped. For example, in a HTML form, if a label is placed too far away from the field it is associated with, they will not appear to be related. Similarity: when elements look similar …
The Fold
A theoretical horizontal line, below which the content of a web page is not visible without scrolling This term is borrowed from the literal horizontal fold in the centre of broadsheet newspapers. In that medium, headlines and other eye-catching content are often placed above the fold line, to be visible when the newspaper is folded in half for display. On …
Five Hats Rack
Information can be organized in five ways: category, time, location, alphabet, continuum / hierarchy The organization of information highly influences how it is understood by users. The Five Hat Racks design principle was originally developed as part of Richard Wurman’s 1989 work on ‘Information Anxiety’, exploring how to increase the amount of information we can grasp, given the digital age’s …