The degree to which websites and web application s are available and usable by people regardless of ability. Web accessibility is often used to describe the right of access to web services and products for the elderly and people with disabilities. In this context, accessibility depends on how a person’s disability or age affects the way they perceive content on …
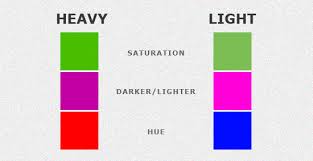
Visual Weight
The ability of a region or element in a composition to draw attention often through contrast or color Elements of a design or image have different degrees of ‘heaviness’ in relation to each other. By ensuring that key elements are ‘heaviest’, the viewer’s attention can be drawn to what is most important. The visual weight can be obvious, such as …
User Testing
Evaluating the usability of a product by observing user behavior. User testing is the process of observing the use of a system in order to discover technical or usability issues. The findings from these studies are then used to improve the system. Though user testing is a discipline in itself, it does not need to be carried out with a …
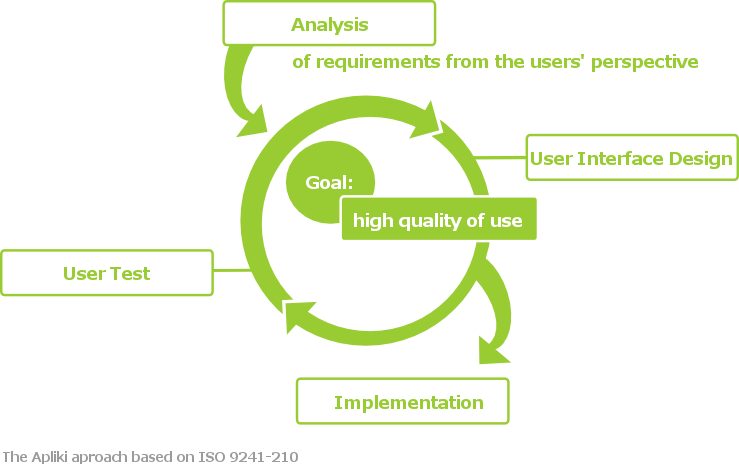
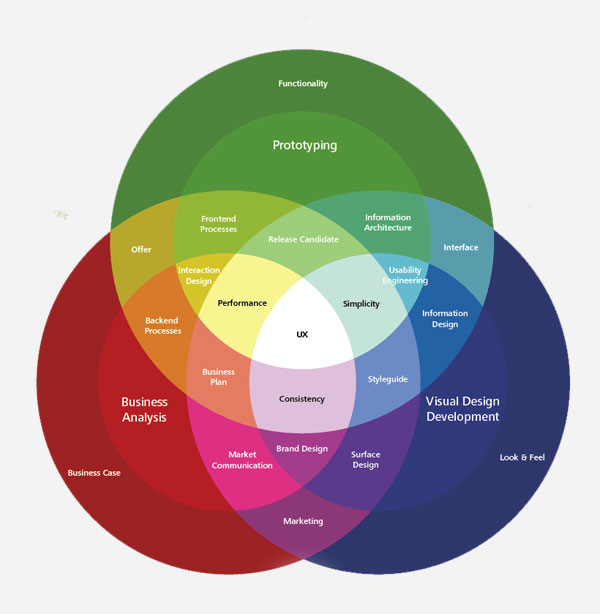
User Experience
A blanket term for all factors which influence the users perception of a product or a service. User experience is often abbreviated to UX, and is also known as ‘experience design’. When interacting with any system, there are many qualities which affect the emotional response of the user. Aesthetics, responsiveness, familiarity and usability are just some of the elements which …
Useability
This judges whether a design helps users achieve specific goals in a particular context with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction. It is often associated with the function of a product as well as being a characteristic of the user interface. It is a key part of the definition of ‘usefulness’ alongside utility, and is composed of five main elements. ‘Learnability’ determines …
URL first design
URLS should be designed in the early stages of website development as users must be able to read, guess and edit them, and it helps designers to define site structure. This principle advocates that URLs should be designed before creating the sitemap, wireframe, or code for any given website. This is because URLs are the ‘one universal syntax’ of the …
Responsive Web Design
Techniques and technologies for optimizing user experience on a wide range of devices The growth of smartphone and tablet devices in recent years has seen the range of screen sizes and resolutions skyrocket. As it would be impractical to build many websites to suit every possible environment, responsive design has emerged as a method for creating single, flexible websites which …
Progressive Enhancement
A design and development technique which delivers essential features regardless of browser capability and advanced features where supported Progressive enhancement is an approach to web design that encourages the use of web technology layers (e.g. HTML, CSS, Javascript, images etc.) in a manner that enables everyone to access the basic content and functionality of a website, regardless of their browser …
Paper Prototyping
Disposable Interface mock-ups sketched on paper for quick iteration and experimentation Website design in its most crude form, this exercise encourages designers and stakeholders to sketch interface concepts on paper to experiment quickly and efficiently. By working roughly with paper and pen, ideas can be tested and discarded before creators become attached to their work. Crucially, a great deal of …
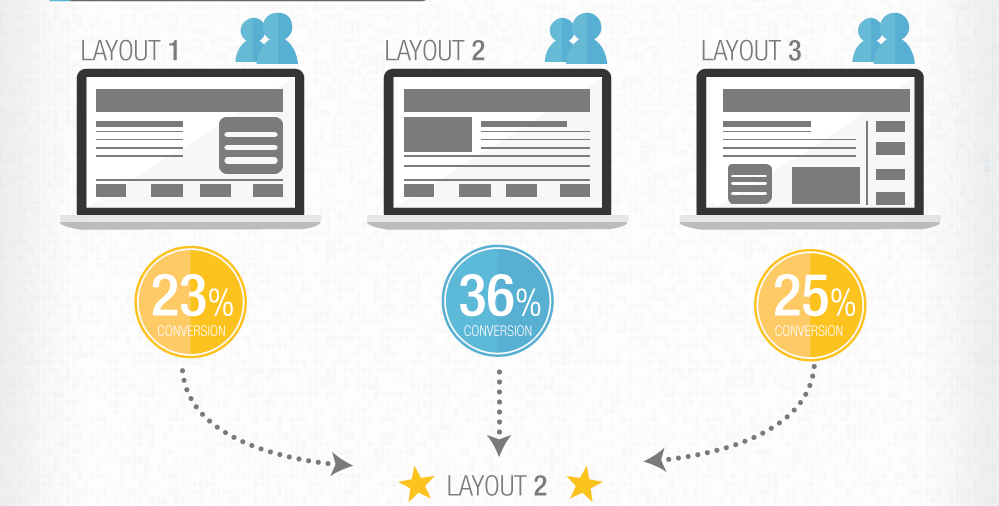
Multi-Variate Testing
Comparing complex multi-variable systems, especially for understanding market perceptions A process for comparing the effects of multiple components of a website in a live environment. This is essentially many comparison tests performed on one page at the same time. A dynamic website can be used to serve up different versions of a page in equal proportions to visitors. The key …